Back for more are you?
Over the past few posts I’ve been covering the new integration between Azure AD and AWS SSO. The first post covered high level concepts of both platforms and some of the problems with the initial integration which used the AWS app in the Azure Marketplace. In the second post I provided a deep dive into the traditional integration with AWS using a non-Azure AD security token service like AD FS (Active Directory Federation Services), what the challenges were, how the new integration between Azure AD and AWS SSO addresses those challenges, and the components that make up both the traditional and the new solution. If you haven’t read the prior posts, I highly recommend you at least read through the second post.

New Azure AD and AWS SSO Integration
In this post I’m going to get my hands dirty and step through the implementation steps to establish the SAML trust between the two platforms. I’ve setup a fairly simple lab environment in Azure. The lab environment consists of a single VNet (virtual network) with a four virtual machines with the following functions:
- dc1 – Windows Active Directory domain controller for jogcloud.com domain
- adcs – Active Directory Certificate Services
- aadc1 – Azure Active Directory Connect (AADC)
- adfs1 – Active Directory Federation Services
AADC has been configured to synchronize to the jogcloud.com Azure Active Directory tenant. I’ve configured federated authentication in Azure AD with the AD FS server acting as an identity provider and Windows Active Directory as the credential services provider.

Lab Environment
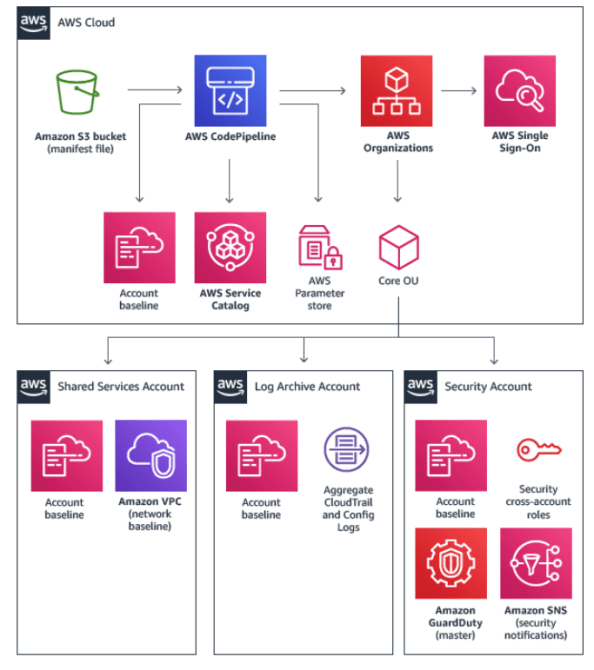
On the AWS side I have three AWS accounts setup associated with an AWS Organization. AWS SSO has not yet been setup in the master account.
Let’s setup it up, shall we?
The first thing you’ll need to do is log into the AWS Organization master account with an account with appropriate permissions to enable AWS SSO for the organization. If you’ve never enabled AWS SSO before, you’ll be greeted by the following screen.

Click the Enable AWS SSO button and let the magic happen in the background. That magic is provisioning of a service-linked role for AWS SSO in each AWS account in the organization. This role has a set of permissions which include the permission to write to the AWS IAM instance in the child account. This is used to push the permission sets configured in AWS SSO to IAM roles in the accounts.

AWS SSO Service-Linked IAM Role
After about a minute (this could differ depending on how many AWS accounts you have associated with your organization), AWS SSO is enabled and you’re redirected to the page below.

AWS SSO Successfully Enabled
Now that AWS SSO has been configured, it’s time to hop over to the Azure Portal. You’ll need to log into the portal as a user with sufficient permissions to register new enterprise applications. Once logged in, go into the Azure Active Directory blade and select the Enterprise Applications option.

Register new Enterprise Application
Once the new blade opens select the New Application option.

Register new application
Choose the Non-gallery application potion since we don’t want to use the AWS app in the Azure Marketplace due to the issues I covered in the first post.

Choose Non-gallery application
Name the application whatever you want, I went with AWS SSO to keep it simple. The registration process will take a minute or two.

Registering application
Once the process is complete, you’ll want to open the new application and to go the Single sign-on menu item and select the SAML option. This is the menu where you will configure the federated trust between your Azure AD tenant and AWS SSO on the Azure AD end.

SAML Configuration Menu
At this point you need to collect the federation metadata containing all the information necessary to register Azure AD with AWS SSO. To make it easy, Azure AD provides you with a link to directly download the metadata.

Download federation metadata
Now that the new application is registered in Azure AD and you’ve gotten a copy of the federation metadata, you need to hop back over to AWS SSO. Here you’ll need to go to Settings. In the settings menu you can adjust the identity source, authentication, and provisioning methods for AWS SSO. By default AWS SSO is set to use its own local directory as an identity source and itself for the other two options.

AWS SSO Settings
Next up, you select the Change option next to the identity source. As seen in the screenshot below, AWS SSO can use its own local directory, an instance of Managed AD or BYOAD using the AD Connector, or an external identity provider (the new option). Selecting the External Identity Provider option opens up the option to configure a SAML trust with AWS SSO.
Like any good authentication expert, you know that you need to configure the federated trust on both the identity provider and service provider. To do this we need to get the federation metadata from AWS SSO, which AWS has been lovely enough to also provide it to us via a simple download link which you’ll want to use to get a copy of the metadata we’ll later import into Azure AD.
Now you’ll need to upload the federation metadata you downloaded from Azure AD in the Identity provider metadata section. This establishes the trust in AWS SSO for assertions created from Azure AD. Click the Next: Review button and complete the process.

Configure SAML trust
You’ll be asked to confirm changing the identity source. There a few key points I want to call out in the confirmation page.
- AWS SSO will preserve your existing users and assignments -> If you have created existing AWS SSO users in the local directory and permission sets to go along with them, they will remain even after you enable it but those users will no longer be able to login.
- All existing MFA configurations will be deleted when customer switches from AWS SSO to IdP. MFA policy controls will be managed on IdP -> Yes folks, you’ll now need to handle MFA. Thankfully you’re using Azure AD so you plenty of options there.
- All items about provisioning – You have to option to manually provision identities into AWS SSO or use the SCIM endpoint to automatically provision accounts. I won’t be covering it, but I tested manual provisioning and the single sign-on aspect worked flawless. Know it’s an option if you opt to use another IdP that isn’t as fully featured as Azure AD.

Confirmation prompt
Because I had to, I popped up the federation metadata to see what AWS requiring in the order of claims in the SAML assertion. In the screenshot below we see is requesting the single claim of nameid-format:emailaddress. This value of this claim will be used to map the user to the relevant identity in AWS SSO.

Back to the Azure Portal once again where you’ll want to hop back to Single sign-on blade of the application you registered. Here you’ll click the Upload metadata file button and upload the AWS metadata.

Uploading AWS federation metadata
After the upload is successful you’ll receive a confirmation screen. You can simple hit the Save button here and move on.

Confirming SAML
At this stage you’ve now registered your Azure AD tenant as an identity provider to AWS SSO. If you were using a non-Azure AD security token service, you could now manually provision your users AWS SSO, create the necessary groups and permissions sets, and administer away.
I’ll wrap up there and cover the SCIM provisioning in the next post. To sum it up, in this post we configured AWS SSO in the AWS Organization and established the SAML federated trust between the Azure AD tenant and AWS SSO.
See you next post!