This is part of my series on Network Security Perimeters:
- Network Security Perimeters – The Problem They Solve
- Network Security Perimeters – NSP Components
- Network Security Perimeters – NSPs in Action – Key Vault Example
- Network Security Perimeters – NSPs in Action – AI Workload Example
- Network Security Perimeters – NSPs for Troubleshooting
Welcome back fellow geeks!
Today I will be continuing my series on NSPs (Network Security Perimeters). In the last post I outlined the problems NSPs were built to solve. I covered how users of Azure have historically controlled inbound and outbound traffic for PaaS (platform-as-a-service) in Azure and the gaps and challenges of those designs. In this post I’m going to dig into the components that make up an NSP, what their function is, how they’re related, and how they work together.
A Quick Review
Before I dive into the gory details of NSP primitives, I want to do a quick refresh on terminology I’ll be using in this post. As I covered in the last post, I divide PaaS services in Azure into what I call compute-based PaaS and service-based PaaS. Service-based PaaS is PaaS where you upload data but don’t control the code executed by the PaaS whereas with compute-based PaaS you control the code executed within the service. NSPs shine in the service-based PaaS realm and that will be my focus for this series.

Securing service-based PaaS with the traditional tooling of IP whitelisting, service whitelisting, resource whitelisting, resource-specific outbound controls (and they are very rare) presented the problems below:
- Issues at scale (IP whitelisting).
- Certain features were not available in all PaaS (resource-based whitelisting or product-specific outbound controls).
- The configuration for inbound network control features lived as properties of the resource and could be configured differently by different teams resulting in inconsistent configurations.
- Logging widely differed across products.
All the challenges above demanded a better more standardized solution, and that’s where NSPs come in.
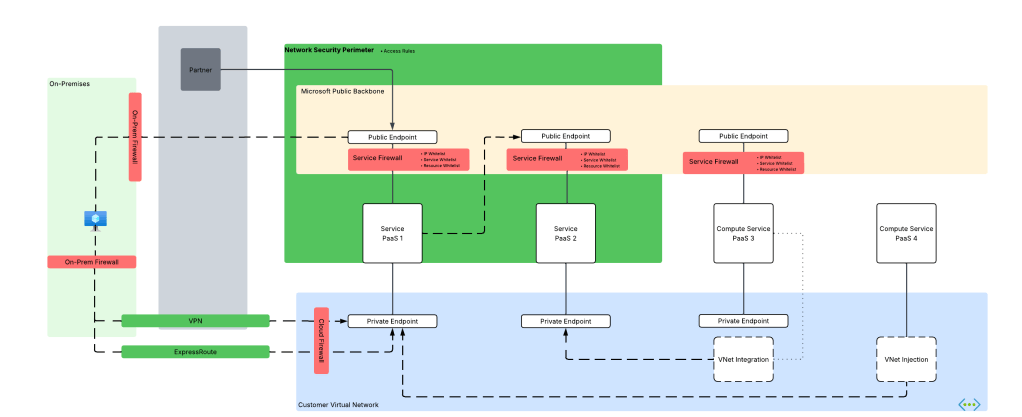
Network Security Perimeter Components
I’m a huge fan of breaking down any technology into the base components that make it up. It makes it way easier to understand how the hell these things work together holistically to solve a problem. Let’s do that.

Network Security Perimeter Hierarchy
At the highest level is the Network Security Perimeter resource. This is what I refer to as a top-level resource, meaning a resource that exists directly under an Azure Resource Provider and is visible under a resource group. The Network Security Perimeter resource exists in the Microsoft.Network resource provider, is regional in nature (vs global), and serve as the outer container for the logic of the NSP.
The resource is very simple and the only properties of note are name, location, and tags.

Profiles
Underneath the Network Security Perimeter resource is the Profile resource. The easiest way to think about a profile is that it’s a collection of inbound and outbound network access rules that you plan to tie to a resource or resources. Each Network Security Perimeter resource can have 1 or more profiles. It’s recommended you have less than 200 profiles, however, I have trouble thinking of a use case for that many unless you’re in an older and more legacy subscription model where you’re packing everything into as few subscriptions as possible (not where you should be these days).
From mucking around with profiles, I can see the use for putting resources in the same NSP into different profiles. For example, I may wrap an NSP around a Storage Account and the Key Vault which holds the CMK (customer-managed key) used to encrypt the Storage Account. I’d likely want one profile for the storage account with a large set of inbound rules and another profile for the Key Vault with a profile with no inbound or outbound rules restricting the Key Vault to be accessed by the Storage Account. My CI/CD pipeline could reach the Key Vault via a Private Endpoint as NSPs DO NOT affect traffic ingressing through the resource’s Private Endpoint. Resources within the same NSP can communicate with each other as long as they’re associated with a managed identity (according to docs, still want to test and validate this myself).

Access Rules
Next up you have the Access Rule resource which exists underneath the Profile resource. This is where the the rubber hits the road. Access rules should be familiar to you old folks like myself as they are very similar to firewall rules (at least today). You have a direction (inbound or outbound) and some type of type of property to filter by. For example, as of the date of this post, inbound traffic can support filtering on subscriptions (very similar to the resource whitelisting in Azure Storage) and IP-based rules (similar to IP whitelisting of traditional service firewall). Outbound traffic can be filtered by FQDN (fully qualified domain name). You can have up to 200 rules per profile (this is a hard limit).
If you’re nosy like I am, you may have glanced at the API reference. Inside the API reference, there are additional items that may someday come to fruition such as email addresses and phone numbers (really curious as to the use cases for these) and service tags (DAMN handy but not yet usable as of the date of this post).

Resource Association
The Resource Association resource exists underneath the Network Security Perimeter. Resource associations connect a supported Azure resource to Network Security Perimeter’s profile and dictate an access mode. There are two documented access modes today which include learning (since renamed transition mode in documentation), and enforced. Transition mode (or learning mode in the APIs) is the default mode and is the mode you’ll start with to understand the inbound and outbound traffic of the resources associated with the NSP. Only after you understand those patterns should you switch to enforced mode. In enforced mode the access rules applied the relevant profile will take effect and all inbound and outbound traffic outside the NSP will be blocked unless explicitly allowed.
Audit mode is a third mode that is available via the API but isn’t mentioned in main public documentation. Your use case for audit mode as far as I can see is if you (say you’re information security) want to audit inbound and outbound traffic out of PaaS resources that are associated to a Network Security Perimeter you do not control.
To answer a few questions that I know immediately popped in my head:
- Yes, you can associate resources to a network security perimeter that is in different a subscription.
- No, you cannot associate a resource to multiple profiles in enforced mode in the same Network Security Group. Associations to other profiles must be configured in access mode.
- No, you cannot associate a resource to multiple profiles in enforced mode in different Network Security Groups. Associations to other profiles must be configured in access mode.

Transition and Enforcement Mode
I want to dig a bit more into transition and enforcement mode and how they affect the resource-level service firewall controls.
In transition mode (which is the default mode) the NSP will evaluate the access rules of the profile the resource is associated with and will log whether the traffic would be allowed or denied (if diagnostic logging is enabled which you most definitely should enable and I’ll cover quickly below but more in depth in a future post) by the NSP and will then fallback to obeying the rules defined in the resource’s service firewall. This is a stellar way for you to get a baseline on how much shit will break with your new rules (and oh yes will shit break for some folks out there).
Once you understand the traffic patterns and design rules around what you want to allow in via the public side of the PaaS, you can flip the resource association to enforced mode. Once you flip that switch, the associated resources will have public access blocked both inbound and outbound. If you have IP whitelisting defined, those rules are ignored. If you checked off the “Allow Microsoft trusted services”, those rules are ignored. As I mentioned above, access through a Private Endpoint is never affected by NSPs as NSPs are concerned with traffic ingressing or egressing from the public sides of the PaaS resource.
It’s worth noting that a new value of the publicNetworkAccess property has been introduced. The publicNetworkAccess property is a property standard to PaaS (I haven’t seen one without it yet). Typically, the two values are either Enabled or Disabled. The property will be typically be set to Enabled if you’re allowing all public access or are restricting it to specific IP addresses, trusted services, specific resources, or service endpoints. It will be typically Disabled when you are blocking all public access and restricting it to Private Endpoints. Note that I use the word typically because this is Azure and there seem to always be exceptions. The new value introduced is SecuredByPerimeter. If you set the publicNetworkAccess property to this the resource is completely locked down to public traffic except for what is allowed in the NSP (even if no NSP is applied). If you plan on transitioning to NSPs fully for controlling public access (once all the resources you need have been onboarded and cross-NSP linking has been introduced) this is the setting you’ll want to go with.
Logging
The best feature of NSPs (in this dude’s opinion) is the logging feature. Like other Azure resources, NSPs support diagnostic settings. These are configured on a per Network Security Perimeter resource and include a plethora of logs categories. These diagnostic settings allow you to turn on detailed logging of traffic that comes in and out of an NSP. This provides you a standard log for all inbound and outbound traffic vs relying on the resource-level logs which can vary greatly per service (again, looking at you AI Search!).
Imagine being able to confirm that a user’s machine is accessing resource over the Microsoft public backbone vs a Private Endpoint and being able to see exactly what IP they’re using to do it. I can’t tell you how helpful this would have been over the past few years where forward web proxies were in use and were incorrectly configured for DNS affecting access to Private Endpoints.
This is such a damn cool feature that it is deserving of its own deep dive post. I’ll be adding this over the next few weeks.
Summing it up
For the purposes of this post, I really want you to take away an understanding of the NSP primitives, what they do, and how they’re related. Do some noodling on how you think you’d use these primitives and what use cases you might apply them to.
Here are some key points to walk away with:
- Network Security Perimeters rules apply only to public traffic, this means traffic incoming to the service’s public IP on the Microsoft public backbone or leaving the service the Microsoft public backbone. They do not affect traffic coming in through a Private Endpoint.
- Resources can be associated to Network Security Perimeters across subscriptions.
- Leverage transition mode (learning mode in the API) to understand what traffic is coming in and going out of your resources over the public endpoints and how your access rules may effect them.
- For resources that support NSPs (and are generally available) think about deploying those resources (it’s only a few as of the date of this post) with the publicAccessProperty set to SecuredByPerimeter at creation to ensure all public network access is controlled by a Network Security Perimeter. This will force you to use NSPs to control that traffic. Auditing or enforcing with Azure Policy would be nice control on top.
- Do some experimentation with the logging provided by NSPs. It will truly blow your mind how useful the logs are to troubleshooting networking issues and identifying network security threats.
- Keep in mind that NSPs will block diagnostic logs from being sent to a Log Analytics Workspace, Storage Account, or Event Hub for any resources within the NSPs. If you use a centralized Log Analytics Workspace model today, you are best off keeping NSPs in transition mode until cross-NSP linking becomes available.
Before I close this out, you’re probably wondering why I didn’t cover the Links resource. Well today, this resource doesn’t do anything and isn’t mentioned in the documentation. If you’re a close observer, you’ll notice the API properties of this resource hint to a possible upcoming feature (I ain’t spoiling anything here since the REST documentation is out there) that looks to provide a feature for NSP to NSP communication. We’ll have to wait and see!
In my next post I’ll walk through three common use cases for NSPs. I’ll cover how the problem was previously solved with service firewall controls and how it can be solved with NSPs. I’ll also walk through the configuration in the Portal and through Terraform. I’ll finish off this series (unless I think of anything else) with a deep dive into NSP logging.
See you next post!







